WE WILL GIVE FULL NOTES OF BIOLOGY FOR PART FIRST YEAR COLLAGE AND HOPE YOU WILL LIKE OUR NOTES AND FOLLOW ON OUR BLOG WE WILL TRY FOR BEST TO BEST AND EASY NOTES FOR YOU
Wednesday, 29 May 2019
FIT AND SLIMIZ: The need for exercise
Tuesday, 1 January 2019
RIBOSOMES

RIBOSOMES Ribosomes are small, dense,rounded and granular particles of the ribonucleoprotein.
DISCOVERY Ribosomes was studied by palade in 995 for the first time.
OCCURRENCE AND DISTRIBUTION: These are small granular structures found in prokaryotes and eukaroyets. They occur either freely in the matrix of mitochondria chloroplast and cytoplasm (i.e, cytoplasmic matrix) or remain attached with the membranes of the endoplasmic reticulum nucleus.
ROLE They carry put proteins synthesis by translating mRNA in the polypeptide chain.
CHEMICAL COMPOSITION
Ribosomes are composed of proteins and ribosomal RNA. Ribosomal RNA in eukaryotes is a four types and three types in prokaryotes. Ribosomes are formed in the nucleolus.

STRUCTURE:
These are small cytoplasmic granules ranging from 20nm-30nm in diameter. Ribosomes are consisting of two sub units of unequal size that fit closely together.
Ribosomes found in eukaryotic cell are 80S, and prokaryotic cell are 70S.
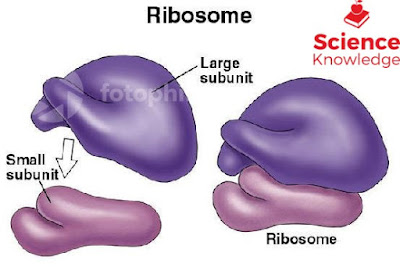
SUBUNITS The subunits are referred as the smaller subunits and the larger subunits. The larger subunits in eukaryotes is 60S while in prokaryotes is 50S. The smaller subunits in eukaryotes is 40S and in prokaryotes 30S.
SVEDBREG UNIT: "S" refers to Svedbreg unit that is the sedimentation rate in ultracentrifuguation.
EUKARYOTIC RIBOSOMES: Its smaller sub unit is 30S and Larger subunit is 50S and complex is 70S.
PROKARYOTIC RIBOSOMES: Its smaller sub unit is 40S and larger sub unit is 60S and complex is 80S.
ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM

ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM Endoplasmic reticulum is an extensive network of interconnected channels and vesicles called cisternae, these membranous channels extends from the nuclear membrane into the cytoplasm. The membrane enclosed space between the cisternae is called the lumen of ER.
TYPES OF ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM On the basis of the presence or the absence of the ribosomes there are two types of ER
SMOOTH ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM The surface of smooth ER is devoid of the ribosomes, and thus called the smooth ER.
FUNCTION OF SMOOTH ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM:
AS A TRANSPORT SYSTEM The endoplasmic reticulum acts as an intracellular circulatory or transporting system. The channels help in the transport of material in the cell.
DETOXIFICATION OF TOXIC SUBSTANCE Smooth ER helps in the detoxification of toxic substance in liver
LIPID METABOLISM: Smooth ER helps in lipid metabolism.
ROUGH ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM: The surface of the rough ER is studded with ribosomes and thus is called as rough endoplasmic reticulum. RER is in direct contact with the nuclear membrane, and RER the nuclear membrane is also studded with ribosomes.
FUNCTION OF ROUGH ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM:
SKELETAL FRAMEWORK:
The endoplasmic reticulum provides an ultra- structural skeleton frame work to the cell and gives mechanical support to the colloidal cytoplasmic matrix.
AS A TRANSPORT SYSTEM:
The endoplasmic reticulum acts as an intracellular circulatory or transporting system.
The channels help in the transport of material in the cell.
PROTEIN SYNTHETIC MACHINERY:
Rough ER helps in the synthesis of proteins.
FORMATION OF NUCLEAR ENVELOP:
The ER membranes from the new nuclear envelope after each nuclear division.
